Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Fe
Fe O
O /Pt heterostructures
/Pt heterostructuresIeda, Junichi; Okayasu, Satoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Kobata, Masaaki; Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Ishida, Masahiko*; Saito, Eiji
IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 58(8), p.1301106_1 - 1301106_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.45(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The combination of spin-driven thermoelectric (STE) devices based on spin Seebeck effect (SSE), and radioactive isotopes as heat sources, has potential as a next-generation method of power generation in applications such as power supplies for space probes. However, there has been very limited knowledge available indicating the irradiation tolerance of spin thermoelectric devices. Through analysis using a heavy ion-beam accelerator and the hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HAXPES) measurements, we show that a prototypical STE device based on Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt heterostructures has tolerance to irradiation of high-energy heavy-ion beams. We used 320 MeV gold ion beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. By varying the dose level, we confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation dose up to
/Pt heterostructures has tolerance to irradiation of high-energy heavy-ion beams. We used 320 MeV gold ion beams modeling cumulative damages due to fission products emitted from the surface of spent nuclear fuels. By varying the dose level, we confirmed that the thermoelectric and magnetic properties of the SSE elements are not affected by the ion-irradiation dose up to 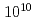 ions/cm
ions/cm fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around
fluence and that the SSE signal is extinguished around 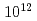 ions/cm
ions/cm , in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. In addition, the HAXPES measurements were performed to understand the effects at the interface of Y
, in which the ion tracks almost fully cover the sample surface. In addition, the HAXPES measurements were performed to understand the effects at the interface of Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt. The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. We share the current understandings of the damage analysis in Y
/Pt. The HAXPES measurements suggest that the chemical reaction that diminishes the SSE signals is enhanced with the increase of the irradiation dose. We share the current understandings of the damage analysis in Y Fe
Fe O
O /Pt for developing better STE devices applicable to harsh environmental usages.
/Pt for developing better STE devices applicable to harsh environmental usages.
Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Kai, Takeshi; Kitajima, Kensei*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Majima, Takuya*; Saito, Manabu*
European Physical Journal D, 74(10), p.212_1 - 212_7, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.64(Optics)Fundamental study of interaction between biomolecules and heavy ions in water is very important to predict an initial stage of radiation biological effects. A heavy ion irradiation experiment into droplet target assumed as a biological system in a vacuum was performed to measure production yields of cations and anions for glycine, which was ejected from the droplet target to the vacuum. However, the production mechanisms have been unknown. The PHITS code adapting ion track structure mode was used to analyze the production mechanisms from the dose evaluation at the surface between the vacuum and the water. It is found that induction yields of ionization and excitation, and dissociative electron attachment involved in the secondary electrons were correlated with the production yields of cations and anions of the glycine. The results provide us newly scientific insights to predict an initial stage of radiation biological effects.
Okayasu, Satoru; Harii, Kazuya*; Kobata, Masaaki; Yoshii, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Ishida, Masahiko*; Ieda, Junichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Applied Physics, 128(8), p.083902_1 - 083902_7, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:19.49(Physics, Applied) C and
C and  He
HeAkeo, Kiyoshi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Akeo, Yoko*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 80, 2015/03
It is known that superoxide dismutases (SOD) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the dismutation of superoxide into oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. Ionizing radiation is known to induce oxidative stress through generation of reactive oxygen species resulting in imbalance of the pro-oxidant and antioxidant in the cells, which is suggested to culminate in cell death. Therefore, we measured the activity of SOD in human RE cells exposed to the He- and C-ion beam. The cells collected at 0, 4, 8, and 24 hr after irradiation were extracted by adding the SOD assay buffer to the pellets, and lysed by several cycles of freezing and thawing. The activity of SOD was measured using a modification of the luminol assay. SOD activity decreased according to duration time after irradiation of He-ion, however, in case of C-ion, it increased at 24 hr after irradiation. The result suggested that that there were the differences of the effects by irradiation on SOD activity between He- and C-ion.
Kitabatake, Satomi*; Ushiroda, Tota*; Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Okahata, Yoshio*; Ito, Atsushi*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 86, 2015/03
Biological effects of high-LET radiation could be understood in terms of the ion track structure. Therefore the evaluation of the contribution of both core and penumbra regions to biological effects is an important issue for the study of high-LET effects. In the present study, we developed a protocol to make a uniform DNA sheet with insoluble nature in aqueous solution, and explored the applicability to the detection of 8-OHdG distributions after heavy-ion irradiation. Water-insoluble DNA sheet was irradiated with proton and neon ion beams at JAEA-Takasaki. After irradiation DNA samples were incubated with an 8-OHdG antibody followed by with a second antibody containing a fluorescence probe. The preliminary results indicated that upon ion irradiation randomly distributed dot-like fluorescence was observed, suggesting that these dots may be from incident ions.
 TiO
TiO
Nakazawa, Tetsuya; Naito, Akira*; Aruga, Takeo; Grismanovs, V.*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Iwase, Akihiro*; Jitsukawa, Shiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(2), p.1398 - 1403, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:92.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Sugai, Hiroyuki; Matsunami, Noriaki*; Fukuoka, Osamu*; Sataka, Masao; Kato, Teruo; Okayasu, Satoru; Shimura, Tetsuo*; Tazawa, Masato*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 250(1-2), p.291 - 294, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:70.56(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated the effects on electrical properties of Al-doped ZnO (AZO) semiconductor films induced by high-energy heavy ion. The AZO films with c-axis on SiO glass substrate were prepared by a RF-sputter-deposition method at 400
glass substrate were prepared by a RF-sputter-deposition method at 400  C. Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy shows that the Al/Zn composition and the film thickness are 4 % and 0.3
C. Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy shows that the Al/Zn composition and the film thickness are 4 % and 0.3  m. We find that the conductivity monotonically increases from 1.5
m. We find that the conductivity monotonically increases from 1.5 10
10 to 8
to 8 10
10 S/cm with increasing the fluence up to 4
S/cm with increasing the fluence up to 4 10
10 /cm
/cm , as already been observed for 100 keV Ne irradiation. The fluence of 100 keV Ne at which the conductivity takes its maximum is 3
, as already been observed for 100 keV Ne irradiation. The fluence of 100 keV Ne at which the conductivity takes its maximum is 3 10
10 /cm
/cm (7 dpa). The dpa of 100 MeV Xe at 4
(7 dpa). The dpa of 100 MeV Xe at 4 10
10 /cm
/cm is estimated as 0.008. Hence, the conductivity increase by 100 MeV Xe ion is ascribed to the electronic excitation effects.
is estimated as 0.008. Hence, the conductivity increase by 100 MeV Xe ion is ascribed to the electronic excitation effects.
Fukuoka, Osamu*; Matsunami, Noriaki*; Tazawa, Masato*; Shimura, Tetsuo*; Sataka, Masao; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Okayasu, Satoru
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 250(1-2), p.295 - 299, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:83(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated the effects on electrical and optical properties of Al-doped ZnO (AZO) semiconductor films induced by high-energy heavy ion. The AZO films with c-axis on SiO glass substrate were prepared by a RF-sputter-deposition method at 400
glass substrate were prepared by a RF-sputter-deposition method at 400  C. Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy shows that the Al/Zn composition and the film thickness are 4 % and 0.3
C. Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy shows that the Al/Zn composition and the film thickness are 4 % and 0.3  m. No appreciable change was observed in optical transparency. We find that the conductivity monotonically increases from 1.5
m. No appreciable change was observed in optical transparency. We find that the conductivity monotonically increases from 1.5 10
10 to 8
to 8 10
10 S/cm with increasing the fluence up to 4
S/cm with increasing the fluence up to 4 10
10 /cm
/cm , as already been observed for 100 keV Ne irradiation. The fluence of 100 keV Ne at which the conductivity takes its maximum is 3
, as already been observed for 100 keV Ne irradiation. The fluence of 100 keV Ne at which the conductivity takes its maximum is 3 10
10 /cm
/cm (7 dpa). The dpa of 100 MeV Xe at 4
(7 dpa). The dpa of 100 MeV Xe at 4 10
10 /cm
/cm is estimated as 0.008. Hence, the conductivity increase by 100 MeV Xe ion is ascribed to the electronic excitation effects.
is estimated as 0.008. Hence, the conductivity increase by 100 MeV Xe ion is ascribed to the electronic excitation effects.
Laird, J. S.; Hirao, Toshio; Onoda, Shinobu; Ito, Hisayoshi
Journal of Applied Physics, 98(1), p.013530_1 - 013530_14, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:80.59(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
 -irradiation on latent tracks of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film
-irradiation on latent tracks of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) filmHiroki, Akihiro; Asano, Masaharu; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Yoshida, Masaru
Chemical Physics Letters, 406(1-3), p.188 - 191, 2005/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:33.01(Chemistry, Physical)The pre-treatment effect of  -irradiation on latent tracks of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) films bombarded with swift heavy ions was investigated by electric conductometry and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation. The Xe-ion bombarded PET films were etched for 6 hours in 0.2 M NaOH aqueous solution at 70
-irradiation on latent tracks of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) films bombarded with swift heavy ions was investigated by electric conductometry and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation. The Xe-ion bombarded PET films were etched for 6 hours in 0.2 M NaOH aqueous solution at 70 C to prepare track-etched membranes. As
C to prepare track-etched membranes. As  -irradiation doses increased in the range of 0-160 kGy, the pore diameter obtained by SEM observation decreased while that obtained by conductometry became large. This inconsistent result between the two methods was due to an increase in the crosslinked region in the latent tracks caused by
-irradiation doses increased in the range of 0-160 kGy, the pore diameter obtained by SEM observation decreased while that obtained by conductometry became large. This inconsistent result between the two methods was due to an increase in the crosslinked region in the latent tracks caused by  -irradiation.
-irradiation.
Sudo, Tomoko*; Ohashi, Kazutoshi*; Sato, Toshimaro*; Ota, Eiji*; Okayasu, Satoru; Sugai, Hiroyuki
Physical Review B, 71(4), p.045211_1 - 045211_7, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.2(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have measured low frequency generation-recombination noise (g-r moise) spectra of a heavily boro-doped diamond crystal over the temperature range 20-300 K. The experimental results show that there are two peaks in the g-r noise spectrum at 120 K and 67 K, respectively. The 120 K peak corresponds to experimental evidence for the existence of hard gap having width of 10.4 meV. We interpret the 67 K peak as evidence for Wigner lattice formation whose gap width is 5.8 meV.
Takahashi, Shuichi*; Yoshida, Masaru; Asano, Masaharu; Nakagawa,Tsutomu*
Polymer Journal, 36(1), p.50 - 53, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:12.7(Polymer Science)The poly(ethylen terephthalate)(PET) membrane, which has a membrane thickness of 12 m, was used in this study. PET is a polymer widely used for fibers, films and bottles. It was assumed that for PET, which is often used as a gas barrier film, it is easy to effect changes in its gas permeability by modification, such as by ion irradiation. Previously, I reported the effect of heavy ion irradiation on the gas permeation of a PET membrane. A portion of the heavy ion irradiated PET membranes exhibited the Knudsen flow during the gas permeation measurements. As a next step, therefore, I applied an etching technique utilizing NaOH solution to control the nanosized pore of the heavy ion irradiated PET membrane. PET membranes irradiated at a fluence of 3
m, was used in this study. PET is a polymer widely used for fibers, films and bottles. It was assumed that for PET, which is often used as a gas barrier film, it is easy to effect changes in its gas permeability by modification, such as by ion irradiation. Previously, I reported the effect of heavy ion irradiation on the gas permeation of a PET membrane. A portion of the heavy ion irradiated PET membranes exhibited the Knudsen flow during the gas permeation measurements. As a next step, therefore, I applied an etching technique utilizing NaOH solution to control the nanosized pore of the heavy ion irradiated PET membrane. PET membranes irradiated at a fluence of 3 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm were etched in 6N or 1N NaOH solution at 60
were etched in 6N or 1N NaOH solution at 60 C. The etching time was controlled to observe the changes in the gas permeation behavior depended on the etchig. This objective has consequently been used to control the Knudsen flow.
C. The etching time was controlled to observe the changes in the gas permeation behavior depended on the etchig. This objective has consequently been used to control the Knudsen flow.
 superconductor by high-energy heavy ion irradiation
superconductor by high-energy heavy ion irradiationSasase, Masato; Okayasu, Satoru; Kurata, Hiroki; Hojo, Kiichi
Journal of Electron Microscopy, 51(Supple), p.S235 - S238, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
 Sr
Sr CaCu
CaCu O
O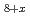 single crystals due to thermal annealing
single crystals due to thermal annealingOgikubo, Koji*; Nakano, M.*; Terai, Takayuki*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Yamawaki, Michio*
Physica C, 357-360(Part.1), p.280 - 283, 2001/09
no abstracts in English
Tonomura, A.*; Hasai, H.*; Kamimura, O.*; Matsuda, T.*; Harada, K.*; Nakayama, Y.*; Shimoyama, J.*; Kishio, K.*; Hanaguri, T.*; Kitazawa, K.*; et al.
Nature, 412(6847), p.620 - 622, 2001/08
Times Cited Count:104 Percentile:94.34(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Direct observation microscopically elucidated the behaviour of vortices in Bi-2212 thin films. The isotropic pinning of vortices by columnar defects at low magnetic fields indirectly inferred by macroscopic magnetization measurements can be explained microscopically as follows; vortex lines are trapped along columns ate temperatures above 19K irrespective of the direction of the applied magnetic field; and at temperatures below 12K vortex lines always penetrate the film perpendicularly to the film plane owing to the increased background pinning compared to the columnar-defect pinning and also because of the demagnetization effect of thin film.
 Cu
Cu Oy under magnetic field
Oy under magnetic fieldIshikawa, Norito; Sueyoshi, T.*; Iwase, Akihiro; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Fujiyoshi, T.*; Miyahara, K.*; Kisu, T.*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 284-288(Part1), p.873 - 874, 2000/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.15(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
 superconductor by high-energy heavy ion irradiation
superconductor by high-energy heavy ion irradiationSasase, Masato; Sato, Takahiro*; Okayasu, Satoru; Kurata, Hiroki; Hojo, Kiichi
Advances in Superconductivity XII, p.314 - 316, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Okayasu, Satoru; Kuroda, N.*; Iwase, Akihiro; Kambara, Tadashi*
Advances in Superconductivity XI, p.287 - 290, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
 Sr
Sr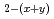 La
La CuO
CuO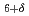 and Bi
and Bi Sr
Sr CaCu
CaCu O
O irradiated with heavy-ions; Correlation between the Bose-glass behavior and the coupling of pancake vortices
irradiated with heavy-ions; Correlation between the Bose-glass behavior and the coupling of pancake vorticesKuroda, N.*; Ishikawa, Norito; Okayasu, Satoru; Iwase, Akihiro; Ikeda, H.*; Yoshizaki, R.*; Kambara, Tadashi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 146(1-4), p.572 - 576, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
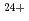 ion irradiation on the superconductive properties and microstructure of EuBa
ion irradiation on the superconductive properties and microstructure of EuBa Cu
Cu O
O thin film
thin filmSasase, Masato*; Okayasu, Satoru; Kurata, Hiroki; Hojo, Kiichi
Surface & Coatings Technology, 103-104, p.360 - 364, 1998/00
no abstracts in English